Understanding Different Types of Road Asphalt
The type of asphalt
can significantly affect the wear and tear of passenger car tires. Smooth and
well-maintained asphalt reduces stress on tires, prolonging their lifespan and
enhancing driving comfort. Conversely, damaged or rough asphalt can accelerate
tire wear and even lead to issues like punctures or blowouts.
Here's a more
detailed breakdown of how different asphalt conditions impact tires:
Smooth Asphalt:
- Minimizes vibrations transmitted to
the tires, thereby reducing stress on their structure.
- Improves driving comfort due to the
reduced vibration.
- Extends tire lifespan by minimizing
stress.
- Less prone to damage such as punctures
or blowouts as it lacks potholes, stones, and other road imperfections.
Damaged or Rough Asphalt:
- Increases vibrations experienced by
the tires, leading to accelerated wear.
- Heightens stress on the tires,
potentially causing damage like cracks or tears.
- Increases the risk of tire punctures
or blowouts from impacts with stones, potholes, or other road hazards.
- May necessitate more frequent tire
maintenance due to quicker wear.
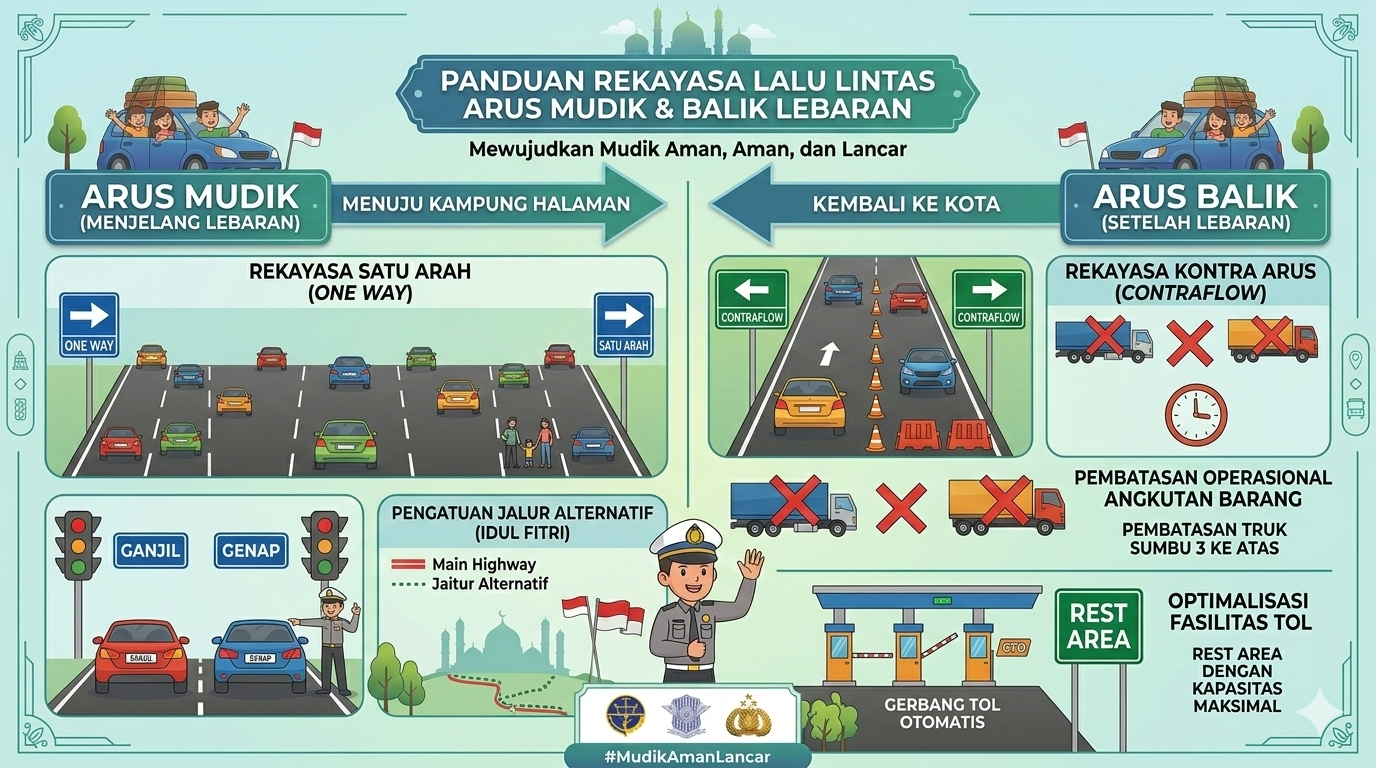
Types of Road Asphalt and Their Effects:
- Asphalt
Roads: Typically smoother and
more even than concrete roads, resulting in less vibration and greater
comfort for both drivers and tires, ultimately extending tire life due to
reduced stress.
- Concrete Roads: Can be rougher and more prone to causing vibrations compared to asphalt roads, potentially leading to faster tire wear due to increased vibration. The increased vibrations might also shorten the lifespan of the suspension system.
Drivers can adapt their driving style and speed when navigating roads with varying asphalt characteristics encountered during travel. Making appropriate adjustments can definitely extend the lifespan of both tires and the vehicle's suspension, ultimately saving costs on spare parts and tire replacements. Hope this helps!
 ID
ID